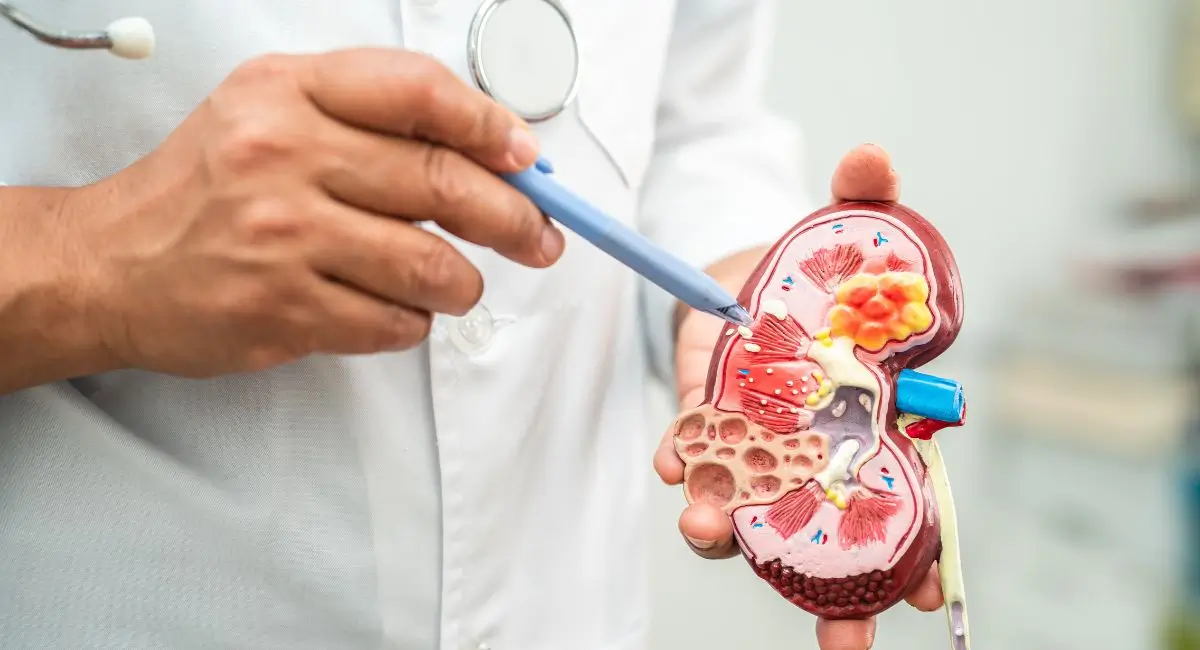
Kidney infections, medically called pyelonephritis, aren’t the same as urinary tract infections (UTI). When bacteria travel up from the bladder and take over your kidneys, they can cause severe signs and symptoms including fever, back ache, and changes in urination. But one question that frequently arises is “Does a kidney infection cause bloating?”
In this complete exploration, we’ll dissect the elaborate relationship between kidney infections and the often overlooked symptom of bloating. We’ll present insights for fitness fanatics, fitness professionals, and clinical professionals.
Contents
- 1 A Basic Understanding Of Kidney Infections
- 2 What Are The Classic Kidney Infections Symptoms
- 3 Why Bloating Is Associated With Kidney Infections
- 4 A Guide To Identifying Kidney Infection Bloating
- 5 Seeking Medical Advice
- 6 Treatment And Prevention
- 7 Final Words – Does A Kidney Infection Cause Bloating ?
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Basic Understanding Of Kidney Infections
Before we explore the connection between bloating and kidney infection, it is essential to recognize what a kidney infection is. Kidney infections are a form of UTI that occurs while bacteria, generally E. Coli from the digestive tract, migrate through the bloodstream and invade the urinary tract or the kidney itself.
The reasons may be multifaceted, including the following:
- A prior urinary tract infection was not adequately treated
- Anatomical factors, such as urinary tract obstructions or vesicoureteral reflux
- A suppressed immune system from diabetes or HIV
Kidney contamination signs and symptoms are pretty distinct, which we will discuss in the next section.
What Are The Classic Kidney Infections Symptoms
When microorganisms reach the kidneys, the immune response creates infection, leading to a host of signs and symptoms:
- Intense back pain, typically on one aspect
- High fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion, especially among the elderly
- Fatigue and weak point
These signs and symptoms can present without bloating, which raises the possibility of them being related.
Why Bloating Is Associated With Kidney Infections
Bloating refers to the sensation of fullness or tightness in the abdominal area, usually associated with fat or fluid retention.
Fluid retention, a common symptom of kidney problems, causes bloating. But the affiliation with kidney infections is not as obvious, and bloating won’t be a trademark symptom.
A Guide To Identifying Kidney Infection Bloating
Given the severity of many kidney infection symptoms, bloating may also be overlooked. It’s critical to distinguish between bloating caused by fluid retention from a kidney infection and unusual gastrointestinal bloating.
To do that, look for these viable signs:
- The feeling of fullness is greater at the aspect of the affected kidney
- Reduced urine output, which could imply kidney impairment
- Bloating is persistent and accompanies other excessive symptoms
If doubtful, a medical assessment can clarify.
Seeking Medical Advice
When experiencing unexplained bloating or an aggregate of symptoms that suggest organ-related problems, well-timed clinical intervention is imperative. Healthcare professionals can run assessments, including blood tests, urinalysis, and imaging, to diagnose or rule out a kidney infection.
Early diagnosis and treatment can save you from complications and help you exercise better.
Treatment And Prevention
As a standard treatment for kidney infections, antibiotics are prescribed. You may also be advised to:
- Take ache relievers
- Stay hydrated
- Use a heating pad for consolation
For prevention, focus on true urinary tract health with these measures:
- Drink lots of water
- Urinate as soon as you feel compelled to
- Wiping from front down to back after rest room usage
- Practicing safe intercourse
A wholesome way of life with these habits can reduce kidney infections and bloating.
Final Words – Does A Kidney Infection Cause Bloating ?
Kidney infections and bloating are complicated. While kidney infections can cause fluid retention and fullness, bloating isn’t always a typical or precise symptom of this situation. However, if you note continual bloating as well as signs and symptoms that may indicate a kidney infection, it’s usually an excellent idea to consult a healthcare expert for a complete examination. Remember, self-diagnosing can lead you down the wrong path, and timely medical intervention is the key to dealing with any fitness situation efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can kidney Issues Cause Belly Bloating?
Yes, kidney problems can result in belly bloating, commonly through fluid retention when the kidneys are not functioning optimally. This malfunction can restrict the body’s ability to remove excess fluid, causing swelling and bloating in the stomach and other parts of the body.
Can UTI Make You Bloated?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) itself may not cause bloating immediately. However, if the UTI progresses to a kidney infection, it could lead to signs such as fluid retention, which can cause bloating. Always consult a healthcare professional if you suspect your bloating is associated with a UTI.
Why Does My Lower Back Hurt And My Stomach Bloat?
Back pain combined with stomach bloating might be symptomatic of various conditions, including urinary tract or kidney infections. These signs and symptoms arise due to the body’s inflammatory response to infection, leading to discomfort and swelling in the affected regions.
Why Do I Constantly Feel Bloated And My Stomach Is Enlarged?
Persistent bloating and stomach expansion may be signs of numerous health problems, including digestive problems to serious conditions like kidney disorder. It’s critical to seek a medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate remedy.
How Do I know If My Bloating Is Critical?
Bloating is considered serious if it is persistent, accompanied by signs such as extreme stomach pain, significant weight loss, vomiting, or changes in urination. These symptoms may indicate a critical underlying problem requiring immediate medical attention.
How To Get Rid Of Bloating In 5 Minutes?
While it is difficult to completely relieve bloating in 5 minutes, positive strategies can offer quick relief. These include taking a brisk stroll, mild stretching activities, or drinking warm water with a lemon to stimulate digestion. For long-term management, figuring out and treating the underlying cause of bloating is vital.
References
National Kidney Foundation. (2023). Understanding kidney infection. Available at: https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/what-are-uti
Mayo Clinic. (2023). Kidney infection. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-infection/symptoms-causes/syc-20353387
Urology Care Foundation. (2023). What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)? Available at: https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/u/urinary-tract-infections
American Kidney Fund. (2023). Kidney disease symptoms. Available at: https://www.kidneyfund.org/kidney-disease/kidney-disease-symptoms
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2023). Urinary Tract Infection. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/uti.html
- Unbiased Fast Lean Pro Reviews: Is It Real or Hype ?
- Understanding Diabetic Fecal Odor: What Does Diabetic Poop Smell Like?
- Nylon Underwear Vs Cotton: Which Is Best For You?
- The Ultimate Guide To Hair Wrap For Sleeping – Transform Your Nights
- What Should You Do When Your Ear Fluttering?
- Unveiling Eyebrow Slits Attraction: A Comprehensive Guide